 The filtering function that arises when a signal is added to itself after having delayed in time is called a comb filter. The resulting frequency response resembles a comb, hence the name.
The filtering function that arises when a signal is added to itself after having delayed in time is called a comb filter. The resulting frequency response resembles a comb, hence the name.
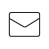
 Two 500Hz sinusoidal tones added. The second is delayed by 1ms, hence the sum is zero. Two 1kHz sinusoidal tones added. The second tone is delayed by 1ms, hence the sum is the double (+6dB).
Two 500Hz sinusoidal tones added. The second is delayed by 1ms, hence the sum is zero. Two 1kHz sinusoidal tones added. The second tone is delayed by 1ms, hence the sum is the double (+6dB).
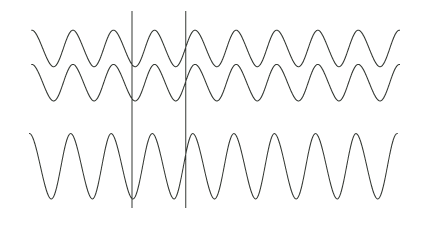
The comb filter function is almost never intentional, but it is heard all the time in sound productions, where it can arise both acoustically and electrically. Acoustically, it typically occurs when the sound on its way from source to receipient takes in part a direct path and in part an indirect path via a single reflective surface. The reflection must be attenuated at least 10dB and preferably 15dB in order for it to not have an effect on the sound field at the recipient position. Electrically, the phenomenon arises when two microphones with a certain distance between them capture the same signal at the level from each microphone is of the same order of magnitude.
Two typical situations in which comb filters arise, either acoustically or electrically.
In genera: All digital signal processing takes time. Thie means in practice that comb filter effects can arise if you loop a signal via, for example, a compressor and combine this signal with the original.
dB Level Frequency - Hz
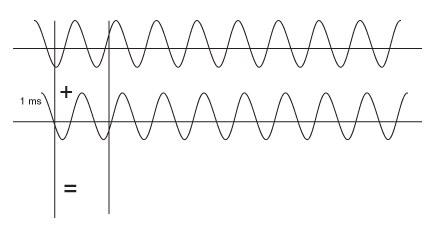
An example of a comb filter created by the combining of two signals with the same amplitude, but with a time delay between them of just 1ms.
It can be seen in a dip occurs due to cancellation at 500Hz, 1.5kHz, 2.5kHz, etc. It can also be seen that the two signals add to double their value (+6dB) at low frequencies and with a full wavelength's delay at 1kHz, 2kHz, 3kHz, etc.
Dip Frequency
Cancellation occurs for a comb filter at all the frequencies where the two signals are in opposite phase. This occurs when the time delay comprises duration of \frac{1}{2}, 1 \frac{1}{2}, 2 \frac{1}{2}, etc, periods. At 1kHz the period is 1ms. Half of the period is 0.5ms. If a time delay of precisely 0.5ms occurs, it means that cancellation will arise, not just at 1kHz, but also at 2kHz, 3kHz, 4kHz and so on.